- Wednesday, October 22, 2025
 ChatGPT Atlas browser, ChatGPT.com
ChatGPT Atlas browser, ChatGPT.com
OpenAI has unveiled ChatGPT Atlas, a web browser built from the ground up with its ChatGPT AI at the core. This innovative browser aims to transform how we use the web by weaving an intelligent assistant into every aspect of browsing. Announced in October 2025 and initially available for macOS (with Windows, iOS, and Android versions on the way), ChatGPT Atlas is positioned as more than just another browser – it’s a rethink of the entire browsing experience powered by AI. OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman described Atlas as a “rare, once-a-decade opportunity to rethink what a browser can be”, underlining the ambition to redefine how we search, work, and get things done online.
What is ChatGPT Atlas?
In essence, ChatGPT Atlas is a full-featured web browser with OpenAI’s ChatGPT AI assistant deeply integrated. It behaves like a typical browser (you can navigate to websites, manage tabs, bookmarks, etc.), but with a constant AI companion ready to assist. Instead of treating ChatGPT as a separate tool, Atlas integrates it directly into the browser interface. The browser can understand what you’re viewing and what you’re trying to accomplish, and it can actively help you without requiring you to copy-paste text or switch to a different app. OpenAI calls it a step toward a “true super-assistant” that understands your world and helps you achieve your goals. In practical terms, ChatGPT Atlas can answer questions in any tab, summarize or explain web pages you’re on, remember your browsing context (if you allow it), and even perform actions online on your behalf. It blurs the line between browsing the web and conversing with an AI that knows your context.
Key Features and Innovations
OpenAI packed Atlas with numerous features that set it apart from a conventional browser. Some of the standout capabilities include:
-
ChatGPT in Every Tab: Each new tab in Atlas doubles as a ChatGPT conversation window. You can ask a question or type a prompt right into a fresh tab and get an AI response alongside search results, without needing to visit a separate site. The new tab page serves as a unified search and chat interface – enter a URL or query, and Atlas will show you web results (including images, videos, news) enhanced with ChatGPT’s context-aware answers.
-
Context-Aware AI Assistant: Atlas’s ChatGPT is aware of your browsing context. With your permission, it knows what page you’re currently viewing, which tabs are open, and even if you’re logged in to a site, enabling it to give relevant, personalized assistance. For example, if you’re shopping or reading an article, you can ask ChatGPT to summarize the product reviews or the article’s key points. This context awareness means more tailored answers – OpenAI notes that Atlas can offer more relevant and personal responses when you’re researching, shopping, or writing online.
-
In-Line Writing Help: If you’re filling out a form, writing an email, or editing a document in the browser, Atlas can act as your writing assistant. Rather than copying text into ChatGPT for help, you can invoke ChatGPT right in the text field to get suggestions or rewrites on the fly. This feature lets Atlas help polish your email drafts, social media posts, or job applications in place – no more jumping back and forth for writing advice.
-
Built-In Memory: One of Atlas’s innovations is an optional browser memory that remembers what you’ve browsed and can resurface that information later. If enabled, ChatGPT Atlas will remember key pages you visited, ideas you explored, or tasks you started – almost like a smart history that the AI can draw upon. This means you can ask things like, “What job postings did I look at last week?” and the browser can recall and summarize them. Importantly, this memory feature is entirely under user control: you can review or delete these saved contexts anytime, and if you clear your history, it clears the AI’s memory of those pages. Those who prefer not to have any AI memory can leave it off and use Atlas just like a standard browser.
-
Natural Language Commands: ChatGPT Atlas lets you control the browser with plain language instructions. Instead of clicking through menus or recalling which tab had what, you can simply tell Atlas what you need. For instance, you might say, “Reopen the travel site I was on yesterday” or “Close all my recipe tabs,” and the browser will comply. This turns mundane browsing tasks into a fluid conversation – effectively letting you navigate or manage tabs without manual effort. It’s a productivity boost aimed at reducing friction in your workflow.
-
Agent Mode (Autonomous Browsing): Perhaps the most groundbreaking feature is Agent Mode, which allows ChatGPT to take actions on the web for you. In this mode (currently a preview available to Plus, Pro, and Business subscribers), the AI can autonomously click links, fill forms, navigate websites, and complete multi-step tasks across tabs on your behalf. For example, you could ask Atlas to book a flight or order groceries online, and it will go through the necessary websites, clicking and typing as needed to complete the task – all while explaining what it’s doing. Sam Altman described it succinctly as the AI “using the internet for you”. This agent can handle complex workflows like reading several documents and summarizing them, planning a trip (researching hotels, flights, etc.), or compiling a report from various sources. It’s like having a digital personal assistant who can operate a web browser. Notably, OpenAI has built-in safeguards: Agent Mode can’t run or install programs, can’t access your files or other apps, and will pause for confirmation on sensitive sites (like banking). Users can also run it in a logged-out incognito mode to limit access to personal data. While powerful, the feature is early and can make mistakes, so Atlas prompts you to supervise and confirm actions as needed.
-
User Control & Privacy: A key design point of Atlas is giving users control over the AI’s access and memories. The browser has a full Incognito Mode, which temporarily signs you out of ChatGPT, ensuring no browsing activity is saved or sent to the AI. Even in normal mode, there’s a handy toggle in the address bar to turn off ChatGPT’s visibility for any given site – when off, the AI cannot read the page or remember anything from it. By default, Atlas does not use your browsing content to train OpenAI’s models. (Users can opt in to contribute browsing data to model training in settings, but that’s off unless you choose otherwise.) The browser also inherits parental controls from ChatGPT: for instance, parents can disable the browser’s memory or agent mode for supervised accounts. All these controls emphasize that you set the rules, deciding how much or how little the AI is involved at any moment.
The ChatGPT Atlas home screen on launch. Atlas’s new tab page doubles as an AI-powered start page. Users can ask ChatGPT questions or type a URL into the unified search bar, and the browser will display results alongside ChatGPT’s answers. It even offers suggested prompts (“Find holiday recipes,” “Research holiday gifts,” “Finish holiday shopping,” etc.) to showcase tasks the AI can help with.
Rethinking the Browser Experience
ChatGPT Atlas isn’t just a collection of new features – it represents a shift in how we think about web browsers. Traditional browsers have changed relatively little in the last decade, but Atlas proposes a new model where an AI agent is deeply embedded in the browsing flow. Instead of the classic routine of manually searching, clicking links, and juggling tabs, Atlas allows a more conversational and goal-driven approach to using the web. OpenAI explains that this project was born from the opportunity AI provides to “rethink what it means to use the web”. Last year, they introduced a web search tool inside ChatGPT, which quickly became one of the platform’s most-used features. That showed the appetite for merging AI with online research. Atlas takes this a step further: rather than bolting an AI onto an existing browser, it’s a browser built around the AI assistant from the start. In fact, the ChatGPT prompt bar in Atlas is intended to feel as central as the URL bar itself eventually – Altman even envisions a future where a chatbot interface replaces the traditional address bar for many tasks.
By integrating ChatGPT into the browser, Atlas significantly reduces friction. There’s no need to copy-paste content into a separate chat window or constantly switch between a browser and an AI app – the AI follows along with you. For example, if you’re reading a dense article, you can ask the built-in ChatGPT to summarize or explain it, and get an answer right there. If you’re comparison-shopping across multiple sites, you can have ChatGPT gather the info and organize it for you. These were things users could do manually with ChatGPT before, but now it’s seamless and integrated. Atlas essentially turns the web into “a collaborative workspace” between you and the AI. It remembers what you care about, helps you find information and take actions, and adapts to your needs as you browse. This level of integration is what makes Atlas distinctive in the current landscape.
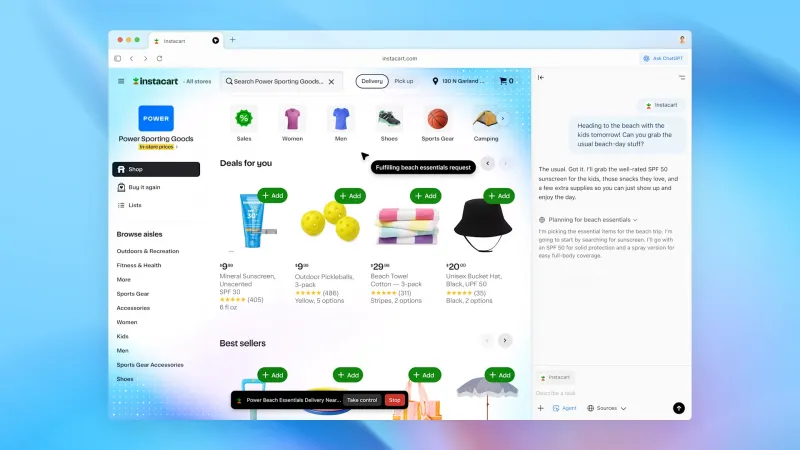
ChatGPT Atlas’s Agent Mode in action. In Agent Mode, Atlas’s built-in AI can autonomously perform complex tasks. In this example, a user asks for help preparing for a beach day, and the AI goes through an online store to add sunscreen, towels and other essentials to a shopping cart (while narrating its steps). This hands-free browsing demonstrates how Atlas can “use the internet for you” when you delegate tasks.
What Makes Atlas Distinctive
With AI features increasingly popping up in browsers, what sets ChatGPT Atlas apart is its AI-first design. Unlike adding a chatbot plugin to an existing browser, Atlas was designed from scratch with ChatGPT at the center of the user experience. This means every design decision – from the new tab layout to the toolbar options – is intended to facilitate intelligent assistance. Atlas doesn’t just answer questions; it proactively supports your workflow. It can recall what you looked at yesterday, help you pick up where you left off, and even execute multi-step tasks across the web for you. Few, if any, browsers have ever had an AI agent that can act on the user’s behalf the way Atlas’s Agent Mode does.
Equally important is the level of integration and control Atlas offers. Because the AI is built in, it can seamlessly blend search with chat, content creation with content consumption, and action with advice. Yet, OpenAI has been careful to give users a say in that integration – you can toggle the AI off for any site or use incognito if you don’t want it involved. Your browsing data stays private by default, addressing a key concern for a tool this powerful. In short, Atlas stands out by reimagining the browser as something more than a passive tool. It becomes an active collaborator, “deeply embedding ChatGPT into every part of the browsing experience” to turn the web into a smarter, more personalized space. It’s a bold vision of browsing where AI isn’t an add-on, but a co-pilot for everything you do online.
Launch Highlights and Future Outlook
The launch of ChatGPT Atlas has been met with considerable interest in the tech community, given OpenAI’s track record. Atlas rolled out globally on October 21, 2025, for all ChatGPT users on Mac (Free, Plus, Pro, and Go tiers), with a beta available for business and enterprise users as well. OpenAI confirmed that Windows and mobile versions are in the works and “coming soon”. This staggered release suggests Atlas is starting in a controlled way (macOS first) before expanding to the much larger Windows and smartphone user bases.
Early commentary from OpenAI frames Atlas as part of a larger shift in how we interact with the internet. “Tabs were great, but we haven't seen a lot of browser innovation since then,” Altman noted during the Atlas announcement, hinting that Atlas’s chat-centric interface could be the next evolution of web navigation. The company also acknowledged the challenges: they are entering a browser market long dominated by major players while adopting a very different approach. Nevertheless, OpenAI appears confident that AI-native features will resonate with users. They plan to iterate quickly on Atlas, with a roadmap that includes multi-profile support and better developer tools for integrating third-party apps and services into the Atlas ecosystem. Website owners are even encouraged to add special tags (like ARIA attributes) to improve how the ChatGPT agent interacts with their sites, indicating that OpenAI sees Atlas’s agentic browsing as a growing trend.
In summary, ChatGPT Atlas introduces a new paradigm for browsing: one where your web browser is also an intelligent assistant. For tech-savvy users and general web surfers alike, Atlas offers a glimpse of a future where browsing isn’t just clicking links, but conversing, delegating tasks, and having a personalized helper navigate the vast information of the internet with you. It’s early days for this AI-driven browser, but its feature set and philosophy make it a distinctive entry in the browser landscape – one that could very well influence how browsers evolve in the coming years
